文章目录:
主播想要练习一下,故花了两个小时模拟了一下23级的C7赛
特意买了个学校机房同款包浆古董慢回弹键盘
A 选择题
第1题
KMP算法的提出者是哪几位___。
- A. D.E.Knuth
- B. J.H.Morris
- C. V.R.Pratt
- D. htunK.E.D
- E. sirroM.H.J
- F. ttarP.R.V
第2题
n个节点(1,...,n)的BST的不同形态数满足___。
- A. $$\Omega\left(\frac{4^n}{n^{\frac{3}{2}}}\right)$$
- B. $$O\left(\frac{4^n}{n^{\frac{3}{2}}}\right)$$
- C. $$\omega(1)$$
- D. $$o(4^n)$$
第3题
以下说法正确的是___。
- A. 均摊分析主要包括聚合分析、记账分析和势能分析。
- B. 均摊分析考虑的是最好情况下的平均时间
- C. 期末考试可以使用共享文档
- D. 使用聚合分析能够分析出Graham's Scan算法的复杂度是 $O(nh)$
第4题
以下说法正确的是___。
- A. Graham's Scan的时间复杂度是 $O(n\lg n)$
- B. Jarvis's March的时间复杂度是 $O(n\lg n)$
- C. Prim算法是贪心思想的应用
- D. 对于网络流图上的容量 $c$ 和流量 $f$,有 $0 \le c(u,v) \le f(u,v)$。
第5题
对于含有负权边但不含负环的图,以下哪些算法能求出正确的最短路?___。
- A. Floyd
- B. Dijkstra
- C. Bellman Ford
- D. 以上都不对
代码
纯蒙,不一定对
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << "ABC" << '\n';
cout << "ABCD" << '\n';
cout << "A" << '\n';
cout << "AC" << '\n';
cout << "AC" << '\n';
return 0;
}B 比赛裁判
猫猫是比赛的裁判!
总共有 $n$ 位选手参加比赛,这些选手编号为 $1,2,\dots,n$。
猫猫宣布,比赛分为 $k$ 轮,在第 $i$ 轮中淘汰编号是 $i+1$ 的倍数的选手。
每轮中分别淘汰了多少位选手呢?
输入
本题测试点包含多组数据。
第一行,一个正整数 $T$($1 \le T \le 10$),表示数据组数。
对于每组数据:
一行,两个整数 $n,k$($2 \le n \le 10^3,\ 1 \le k < n$)。
输出
对于每组数据:
输出一行,$k$ 个整数。第 $i$ 个整数表示第 $i$ 轮中淘汰的选手数量。
输入样例
2
5 3
7 6输出样例
2 1 0
3 1 0 1 0 1代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n;
int t;
int k;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> v(n+3, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= k ;i++){
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(v[j]==0 && j%(i+1)==0){
sum++; v[j] = 1;
}
}
cout << sum << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}C 车厢调度
题目描述
猫猫是火车站调度员!
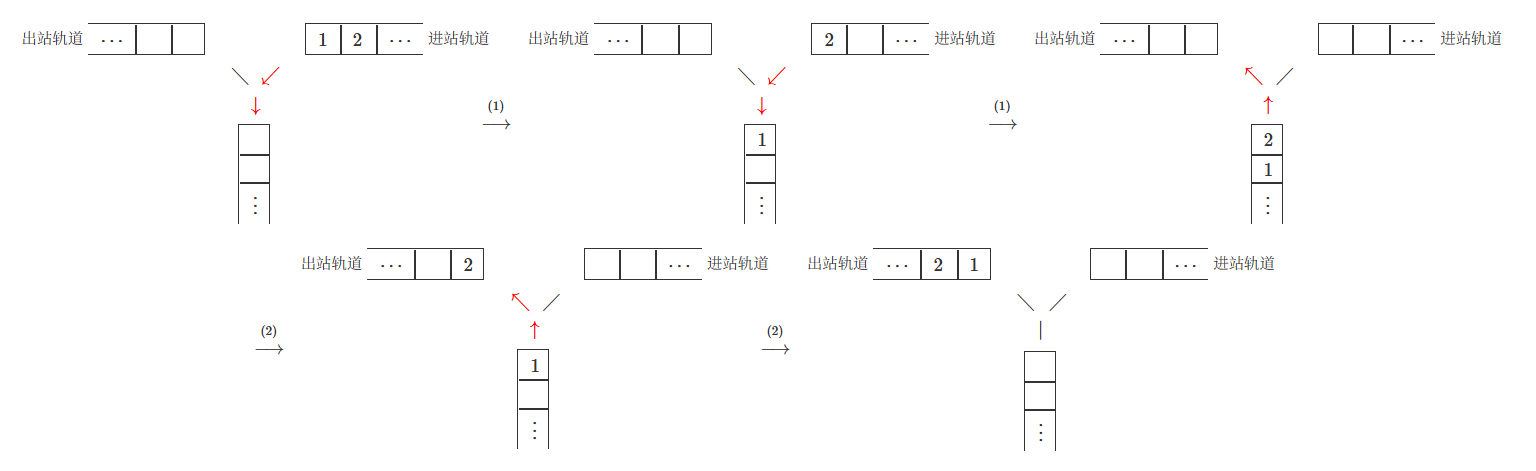
猫猫需要利用一条 $Y$ 形轨道调度火车车厢,$Y$ 形轨道右侧连接进站轨道,左侧连接出站轨道。
具体来说,火车停靠在进站轨道,共有 $n$ 节车厢,车厢的编号依次是 $1,2,\dots,n$。最终火车需要停靠在出站轨道,并且车厢编号依次为 $p_1,p_2,\dots,p_n$。
利用 $Y$ 形轨道,猫猫每次可以进行以下两种操作之一:
- 将当前进站轨道最靠近道岔的车厢移入 $Y$ 形轨道。
- 将 $Y$ 形轨道最靠近道岔的车厢移入出站轨道。
例如按以下方式,可以将进站轨道停靠的车厢 $1,2$,变为出站轨道停靠的车厢 $2,1$。
猫猫想知道,能否只通过这两种操作将火车按照车厢 $p_1,p_2,\dots,p_n$ 的顺序停靠在出站轨道呢?
输入
本题测试点包含多组数据。
第一行,一个正整数 $T$($1 \le T \le 20$),表示数据组数。
对于每组数据:
- 第一行,一个正整数 $n$($1 \le n \le 10^4$),表示车厢数量。
- 第二行,$n$ 个互不相同的正整数 $p_1,\dots,p_n$($1 \le p_i \le n$),表示目标车厢顺序。
输出
对于每组数据:
输出一行,若只通过给出的两种操作能将车厢调度为目标顺序,则输出 YES;否则输出 NO。
输入样例
3
2
2 1
4
1 3 2 4
4
3 1 2 4输出样例
YES
YES
NO提示
样例中的第一组数据即是题目描述中给出的例子。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t, n;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
stack<int> s3;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
int v;
cin >> v;
s1.push(v);
}
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
if(!s2.empty() && s2.top() == i){
s2.pop();
s3.push(i);
continue;
}
else{
while(!s1.empty()){
int top = s1.top(); s1.pop();
if(top == i){
s3.push(i); goto nxt;
}else{
s2.push(top);
}
}
cout << "NO\n";goto nnxt;
}
nxt:{}
}
cout << "YES\n";
nnxt:{}
}
return 0;
}D 数列配对
题目描述
猫猫正在与算法激烈搏斗!
猫猫遇到了一道算法问题,并找到了你求助。问题是这样的:
小 A 手上有 $n$ 个整数 $a_1,a_2,\dots,a_n$,小 B 手上有 $n$ 个整数 $b_1,b_2,\dots,b_n$。猫猫每次可以从小 A 手上拿走一个整数 $a_{p_i}$,并从小 B 手上拿走一个整数 $b_{q_i}$,如果 $a_{p_i} < b_{q_i}$ 则能成功将这两个整数配成一对,否则无法配对。
小 A 和小 B 手上的整数最多能配成多少对呢?
输入
第一行,一个正整数 $n$($1 \le n \le 10^5$)。
第二行,$n$ 个整数 $a_1,a_2,\dots,a_n$($0 \le a_i \le 10^9$)。
第三行,$n$ 个整数 $b_1,b_2,\dots,b_n$($0 \le b_i \le 10^9$)。
输出
输出一行,一个整数,表示最多配对数量。
输入样例
5
1 5 3 4 7
0 2 3 6 6输出样例
3提示
样例中可以将小 A 的 $1,4,5$ 分别与小 B 的 $3,6,6$ 配对,可以证明这种方案有最多的配对数量。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[100009], b[100009];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cin >>b[i];
}
sort(a, a+n);
sort(b, b+n); int i = 0; int j = 0;
int sum = 0;
while(i < n && j < n){
if(a[i] < b[j]){
sum++;
i++; j++;
}else j++;
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}E 复习安排
题目描述
猫猫即将开始紧张刺激的考期!
考期总共有 $n$ 天,猫猫有 $k$ 门课需要考试。对于第 $i$ 门课,如果想顺利通过考试,必须在考期的第 $l_i$ 天到第 $r_i$ 天全身心投入这门课的复习,不能复习其他课程,否则就会挂科。
猫猫最多能通过多少门课的考试?
输入
本题测试点包含多组数据。
第一行,一个正整数 $T$($1 \le T \le 5$),表示数据组数。
对于每组数据:
- 第一行,两个正整数 $n,k$($1 \le n \le 10^5,\ 1 \le k \le n$),分别表示考期天数和课程数。
- 接下来 $k$ 行,每行两个正整数 $l_i,r_i$($1 \le l_i \le r_i \le n$),表示通过第 $i$ 门课的考试所需的复习起止天数。
输出
对于每组数据:
输出一行,一个整数,表示最多能通过的考试数量。
输入样例
2
8 4
1 1
2 4
4 5
6 8
5 3
1 3
2 4
3 5输出样例
3
1代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, k, t;
int sum = 0;
pair<int, int> lesson[100009]; // r, l
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 0; i<k; i++){
cin >> lesson[i].second >> lesson[i].first;
}
sum = 0;
sort(lesson, lesson+k);
int last = -2e9;
for(int i = 0 ; i< k;i++){
pair<int, int> x = lesson[i];
// cout << x.second << x.first << '\n';
if(x.second > last){
sum++;
last = x.first;
}
}
cout << sum << '\n';
}
return 0;
}F 数字魔法
题目描述
猫猫学了一个神奇的数字魔法!Abracadabra!
猫猫有一个长度为 $n$ 的数列 $a_1,\dots,a_n$,每次可以对数列施展以下数字魔法:
- 选择数列中相邻两个数 $x,y$,将数列中这两个数替换为一个数 $|x-y|$。
数列每次被施展魔法之后长度都会减少 $1$,因此 $n-1$ 次魔法之后数列中只剩一个数。由于每次可以选择数列中不同位置施展魔法,不同方案中最后剩下的数不一定相同。猫猫想知道所有可能情况中,最后剩下的数的最小值和最大值分别是多少。
输入
第一行,一个整数 $n$($1 \le n \le 50$),表示数列长度。
第二行,$n$ 个整数 $a_1,\dots,a_n$($0 \le a_i \le 50$)。
输出
一行,两个整数,分别表示所有可能情况中最后剩下的数的最小值和最大值。
输入样例
3
2 3 4输出样例
1 3提示
对于样例,总共有两种不同的施展魔法的方案。第一种方案是:
- $[2,3,4]\to[2,1]$
- $[2,1]\to[1]$
第二种方案是:
- $[2,3,4]\to[1,4]$
- $[1,4]\to[3]$
因此最后剩下的数最小为 $1$,最大为 $3$。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[56][56][56];
int a[56];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
dp[i][i][a[i]] = 1;
}
for(int l = 2; l <= n; l++){
for(int i = 1; i <= (n - l + 1); i++){
int left = i; int right = i + l - 1;
int mid = left;
while(mid < right){
for(int w1 = 0; w1 <= 50; w1++)
for(int w2 = 0; w2 <= 50; w2++)
if(dp[left][mid][w1]!=0 && dp[mid + 1][right][w2]!=0) dp[left][right][abs(w1 - w2)]++;
mid++;
}
}
}
int mmin = 114514, mmax = -114514;
for(int i = 0; i <= 50; i++){
if(dp[1][n][i] > 0){ mmin = min(mmin, i); mmax = max(mmax, i);}
}
cout << mmin << ' ' << mmax;
return 0;
}G 收作业!
题目描述
猫猫是《猫科动物野外生存指南》课程的助教!
课程共有 $n$ 位小猫同学,这些同学依次以 $1,\dots,n$ 编号,助教以 $n+1$ 编号。同学们需要将作业交给助教,但由于很多同学不认识助教,所以会委托它们认识的其他同学转交作业。
具体来说,这 $n+1$ 只猫之间共有 $m$ 对猫相互认识。在第 $i$ 对关系 $(u_i,v_i,c_i)$ 中,编号为 $u_i$ 的猫与编号为 $v_i$ 的猫互相认识,并且两只猫之间传递作业的代价是 $c_i$。除了给定关系之外,任意两只猫之间互相不认识。同学们通过进行多次以下操作,将作业交给助教:
- 选定一对关系 $(u_i,v_i,c_i)$,其中一只猫将它手上的所有作业传递给另一只猫,这一操作的代价是 $c_i$。
最终助教手上有所有同学的作业时结束操作。同学们想知道,将所有同学的作业交给助教需要的最小代价和是多少?
输入
第一行,两个正整数 $n,m$($1 \le n \le 10^5,\ 1 \le m \le 2\times 10^5$),分别表示同学数量,以及关系数量。
接下来 $m$ 行,每行三个正整数 $u_i,v_i,c_i$($1 \le u_i, v_i \le n+1,\ 1 \le c_i \le 10^6$),分别表示互相认识的猫的编号,以及这两只猫之间传递作业的代价。
保证每只猫都能将作业交给助教。
输出
一行,一个正整数,表示交作业所需的最小代价和。
输入样例
3 5
1 2 3
1 3 2
3 2 4
3 4 1
2 4 1输出样例
4代码
最小生成树
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
const int N = 100005;
const int M = 400005;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Edge{
int to, w, next;
}e[M];
int cnt_E = 0;
int head[N];
void init(){
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
}
void addEdge(int x,int y, int w){
e[cnt_E].next = head[x];
e[cnt_E].to = y;
e[cnt_E].w = w;
head[x] = cnt_E++;
}
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
long long prim(int n, int start){
long long dis[N];
bool vis[N];
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> q;
dis[start] = 0;
q.push({0, start});
long long res = 0;
long long cnt = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
long long d= q.top().first;
long long u = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
res+=d;
cnt++;
for(int i = head[u]; i!=-1; i = e[i].next){
long long v= e[i].to;
long long w= e[i].w;
if(!vis[v] && w < dis[v]){
dis[v] = w;
q.push({dis[v], v});
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
init();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int uu, vv ,cc;
cin >> uu >> vv>>cc;
addEdge(uu, vv, cc);
addEdge(vv, uu ,cc);
}
cout << prim(n+1, n+1);
return 0;
}H 路线规划
题目描述
猫猫是幼儿园园长!
幼儿园的小猫们准备前往公园秋游。城里共有 $n$ 个路口,幼儿园位于 $1$ 号路口,公园位于 $n$ 号路口。$m$ 条单向道路连接着这些路口,从 $u_i$ 号路口可以沿第 $i$ 条单向道路前往 $v_i$ 号路口。
猫猫注意到,如果有两只小猫前往公园的路线经过了相同的道路,那么它们会在这条道路上打架。需要注意的是,经过相同的路口不会打架。
猫猫想知道,在不发生打架的前提下,最多能有多少只小猫前往公园呢?
输入
第一行,两个正整数 $n,m$($1 \le n \le 500,\ 1 \le m \le 10000$),分别表示路口数量与单向道路的数量。
接下来 $m$ 行,每行两个整数 $u_i,v_i$($1 \le u_i, v_i \le n$),表示一条从 $u_i$ 到 $v_i$ 的单向道路。
注意可能有多条不同的道路连接 $u_i$ 与 $v_i$。
输出
一行,一个整数,表示在不发生打架的前提下,最多能有前往公园的小猫数量。
输入样例
4 5
1 3
3 4
3 2
1 2
2 4输出样例
2提示
在样例中,第一只小猫沿路线 $1 \to 2 \to 4$ 前往公园,第二只小猫沿路线 $1 \to 3 \to 4$ 前往公园。
代码
最大流
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
const int N = 505;
const int M = 5005;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Edge{
int to, w, next;
}e[M];
int cnt_E = 0;
int head[N];
void init(){
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
}
int dep[N];
int cur[N];
void addEdge(int x,int y, int w){
e[cnt_E].next = head[x];
e[cnt_E].to = y;
e[cnt_E].w = w;
head[x] = cnt_E++;
}
bool bfs(int S, int T){
memset(dep, -1, sizeof(dep));
queue<int> q;
dep[S] = 0;
q.push(S);
memcpy(cur, head, sizeof(head));
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = e[i].next){
int v= e[i].to;
int w = e[i].w;
if(w > 0 && dep[v] == -1){
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dep[T] != -1;
}
int dfs(int u, int limit, int T){
if(u == T || limit == 0) return limit;
int flow = 0;
for(int &i = cur[u]; i!=-1; i = e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
int w = e[i].w;
if(dep[v] == dep[u] + 1 && w > 0){
int f = dfs(v, min(limit, w), T);
if(f > 0){
e[i].w -= f;
e[i ^1].w += f;
flow += f;
limit -= f;
if(limit == 0) break;
}
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic(int S, int T){
int max_flow = 0;
while(bfs(S,T)){
max_flow += dfs(S, INF , T);
}
return max_flow;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
init();
for(int i = 1; i <= m ;i++){
int ui, vi;
cin >> ui >> vi;
addEdge(ui, vi, 1);
addEdge(vi, ui, 0);
}
cout << dinic(1, n) << endl;
return 0;
}I 数列询问
题目描述
猫猫在书上看到了一个神奇的名词——卷积!
猫猫有两个数列,一个是长度为 $n$ 的数列 $a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n$,另一个是长度为 $m$ 的数列 $b_1,b_2,\ldots,b_m$。
猫猫有 $q$ 个询问。在第 $i$ 个询问中,猫猫给出正整数 $k$,你需要回答下式的值:
其中 $1\le i\le n,\ 1\le j\le m$。
输入
第一行,三个正整数 $n,m,q$($1\le n,m\le 10^5,\ 1\le q\le 2\times 10^5$),分别表示数列 $\{a\}$ 的长度、数列 $\{b\}$ 的长度,以及询问个数。
第二行,$n$ 个非负整数 $a_1,\ldots,a_n$($0\le a_i\le 10$)。
第三行,$m$ 个非负整数 $b_1,\ldots,b_m$($0\le b_i\le 10$)。
接下来 $q$ 行,每行一个正整数 $k$($1\le k\le 2\times 10^5$),表示一个询问。
输出
输出共 $q$ 行。对于每个询问,输出一行,一个整数,表示
的值。
输入样例
3 4 2
1 2 3
0 1 2 3
3
5输出样例
1
10提示
对于样例中的第一个询问,答案为 $a_1b_2+a_2b_1=1$。
对于样例中的第二个询问,答案为 $a_1b_4+a_2b_3+a_3b_2=10$。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int MAXN = 262144+5;
struct Complex{
double x, y;
Complex(double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y){}
Complex operator+(const Complex &b) const {return Complex(x+b.x, y+b.y);}
Complex operator-(const Complex &b) const {return Complex(x- b.x, y-b.y);}
Complex operator*(const Complex &b) const {return Complex(x*b.x-y*b.y, x*b.y+y*b.x);}
};
void fft(Complex *a, int n, int type){
static int rev[MAXN];
static int last_n = 0;
if(n!= last_n) {
last_n = n;
int bit = 0;
while((1<<bit)<n) bit++;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) |((i & 1) << (bit - 1));
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(i < rev[i]) swap(a[i], a[rev[i]]);
}
for(int mid = 1; mid < n; mid <<= 1){
Complex wn(cos(PI/mid),type*sin(PI/mid));
for(int R = mid << 1, j = 0; j<n; j+= R){
Complex w(1,0);
for(int k = 0; k < mid; k++, w = w*wn){
Complex x = a[j + k];
Complex y = w * a[j + k + mid];
a[j + k] = x + y;
a[j + k + mid] = x - y;
}
}
}
if(type == -1){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i].x /= n;
}
}
int n, m , q;
Complex a[MAXN], b[MAXN];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i].x;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) cin >> b[i].x;
n--; m--;
int limit = 1;
while(limit <= n + m) limit <<= 1;
fft(a, limit, 1);
fft(b, limit, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < limit; i++) a[i] = a[i]*b[i];
fft(a, limit, -1);
while(q--){
int k;
cin >> k;
cout << (int)(a[k - 2].x + 0.5) << '\n';
}
}J 优秀数对
题目描述
猫猫发现了好多字符串!
猫猫有 $n$ 个仅包含小写英文字母的字符串 $S_1,\ldots,S_n$。如果字符串 $S_i$ 是 $S_j$ 的子串($1\le i,j\le n$),那么称有序对 $(i,j)$ 是优秀的。对于 $1\le i,j\le n$,$(i,j)$ 中总共有多少个优秀的数对呢?
称字符串 $S_i$ 是 $S_j$ 的子串,当且仅当从 $S_j$ 删去某个可以为空的前缀与某个可以为空的后缀之后,可以得到 $S_i$。
例如 $abc$ 是 $dabc$ 的子串,但 $abc$ 不是 $adbd$ 的子串。
输入
第一行,一个正整数 $n$($1\le n\le 500$),表示字符串的数量。
接下来 $n$ 行,每行一个仅包含小写英文字母的字符串 $S_i$。
保证所有字符串长度之和不超过 $5\times 10^4$。
输出
一行,一个整数,表示优秀数对的数量。
输入样例
4
ab
ab
abab
dabc输出样例
10提示
样例中优秀数对有 $(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4),(3,3),(4,4)$,共有 $10$ 对。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
string s[509];
long long ans = 0;
bool cmp(string a, string b){
return a.length() < b.length();
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s[i];
}
sort(s, s+n, cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ans += 1;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++){
if(s[j].find(s[i]) != string::npos){
ans ++;
//cout << i << ' ' << j << '\n';
if(s[j].length() == s[i].length()) ans++;
}
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}K 再见七海
题目描述
猫猫即将踏上新的征程!
猫猫即将出海远航,但不幸的是猫猫不会游泳。
在 $\mathbb{R}^2$ 海洋上漂浮着 $n$ 个浮标,第 $i$ 个浮标的坐标是 $(x_i,y_i)$。海浪把这些浮标冲得很分散,因此这些浮标的坐标都是随机的。
猫猫想从这些浮标中选择三个浮标搭建救生筏,所以希望这三个浮标之间两两以线段连接之后,所形成的三角形面积尽可能的大。
最大的三角形面积是多少呢?
输入
第一行,一个正整数 $n$($3\le n\le 10^5$),表示浮标数量。
接下来 $n$ 行,每行两个整数 $x_i,y_i$($0\le x_i,y_i\le 10^6$),表示浮标的坐标。
保证没有多个浮标坐标相同。保证坐标均是随机生成的。
输出
一行,一个保留一位的实数,表示浮标形成的三角形的最大面积。
输入样例
5
0 0
1 0
0 1
1 2
2 1输出样例
1.5代码
计算几何题,还没做出来